One document referred by everyone – Patent examiner, Licensee, Competitor, Lawyers, Judge, Public/Peers – GETTING IT RIGHT IS IMPORTANT.
Why ‘Your Patent Team’ for Patent Registration in India
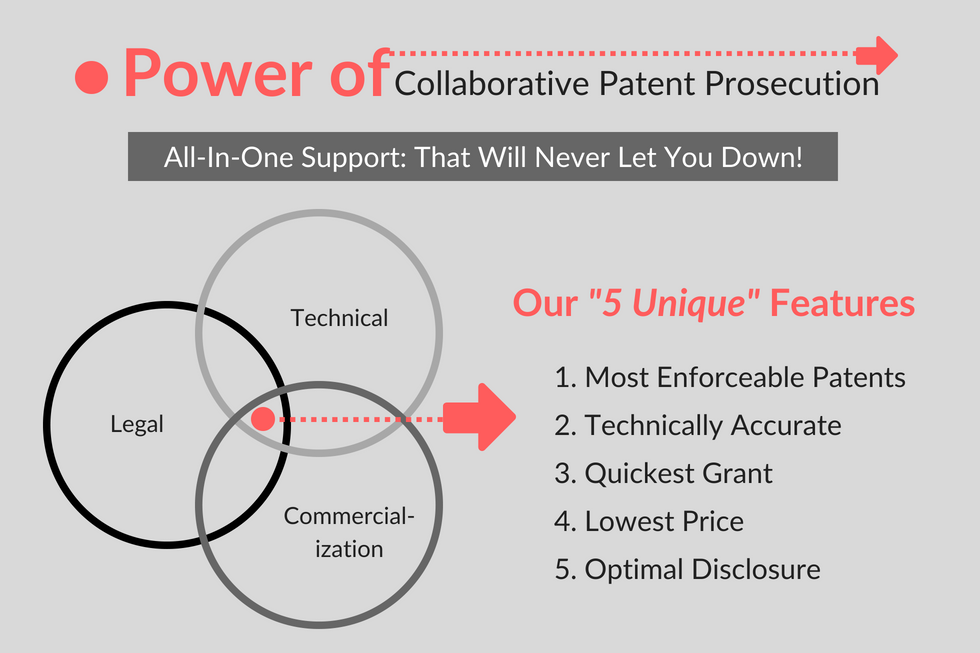
Leverage the Power of Collaborative Patent Prosecution
- YPT is a Team of 225+ technology/industry experts who speak inventor`s language and having deep understanding of Indian and Global patent laws.
- YPT utilizes its knowledge of both patent prosecution process and patent enforcement to draft applications that are enforceable (even 20 years from now) yet sail through the prosecution saving you lot of money.
- YPT always keeps client’s interest first and is always frugal with client’s resources. Ethics is #1 priority for YPT and we will never misguide you.
- YPT ensures that you not just get a certificate after grant of patent rather you practically benefit from your protection. We will walk with you on-the-ground to make it happen.
- YPT has unique understanding of global and industry wide IP best practices as it has supported 1,000+ clients from 45+ countries in multiple technology areas ranging from complex subject matters in life sciences/engineering/ICT to simple household inventions.
- YPT has in-depth understanding of working style of each of the four patent offices in India and also of their staff members.
- YPT has a good network within Indian Patent Office for expedited and accurate information.
Finally, YPT may not seem to be the cheapest option available but we guarantee that :
- You will have the strongest and broadest possible protection.
- You will end up saving lot of money during prosecution and after grant.
Get In Touch / Request Free Consultation
About Your Patent Team (YPT)

Patent Classification
The patent system in India is governed by the Patents Act, 1970 (No.39 of 1970) as amended by the Patents Amendment Rules 2006 with effect from 05-05-2006. Under this Act, there are 3 types of patent protection in India. They are as follows:
- Ordinary Application: Application filed without claiming any priority or any reference to other application. It can either be Provisional or Non-Provisional application. Pre-requisites of both the applications differ from each other. The basic aim of filing Provisional Application is to claim a “Priority Date” for the application when the claims and specifications are in under-process stage. Non-Provisional application or complete application includes all the claims, scope, and specification of the invention in a completed/final format. It must be filed within 12 months or else it will be treated as abandoned.
- Convention Application: Applications filed after claiming priority date (according to similar application filed in same or similar domain) in one or more convention countries, within 12 months of filing the similar application in convention country, is convention application.
- Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) National Phase Application: International patent treaty that provides patent protection in more than one country, which is effective up to 138 countries. National phase application has to be filed in the targeted country within the specified time period of PCT (30/31 months after priority date), depending upon the rules within specified country.
Eligibility Criteria for Patentable Inventions
Applications demanding patent protection for their invention must fulfill the following pre-requisite conditions as per Patent Laws:
- Novelty: The invention must have some new and advanced features that are unknown to the body holding all the existing technical knowledge.
- Non-obvious or inventive step: The invention must not be derivative of any existing invention, derived simply by applying ordinary skills which is so obvious to be concluded by any person. The invention must be invented by a person having significant amount of technical knowledge and must bear observable results that proves that it is completely new.
- Industrial applicability: The invention must bear the ability to prove useful enough for industrial applications instead of satisfying only theoretical aspects.
- Patentability: The invention must be considered as patentable under the territorial laws.
- Clarity: The invention must be written in clear or well stated language so that even an ordinary person having limited skill for that subject could be able to understand the concepts invented.
Application for patent protection can be applied from an inventor or researcher, assignee, or a legal representative of deceased inventor or assignee. It is even permitted to submit an Application can be jointly by two or more corporations as assignees, and alone or jointly by the inventor.
Eligibility Criteria for Non-Patentable Inventions
According to Section 3 of the Indian Patents Act, 1970 the following inventions are not patentable in India:
- An invention, that is frivolous or that claims anything obviously contrary to well established natural laws;
- An invention, the primary or intended use of which would be contrary to law or morality or injurious to public health;
- The mere discovery of a scientific principle or the formulation of an abstract theory;
- The mere discovery of any new property or new use for a known substance or of the mere use of a known process, machine or apparatus unless such known process results in a new product or employs at least one new reactant;
- A substance obtained by a mere admixture resulting only in the aggregation of the properties of the components thereof or a process for producing such substance;
- The mere arrangement or re-arrangement or duplication of known devices, each functioning independently of one another in a known way;
- A method of agriculture or horticulture;
- Inventions relating to atomic energy.
- Any process for the medicinal, surgical, curative, prophylactic or other treatment of human beings or animals.
- Plants and animals in whole or any part thereof other than microorganisms.
- Mathematical or business method or a computer program per se or algorithms.
- Literary, dramatic, musical or artistic works, cinematographic works, television productions and any other aesthetic creations.
- Mere scheme or rule or method of performing a mental act or playing game.
- Presentation of information.
- The topography of integrated circuits.
- An invention which in effect, is traditional knowledge or is based on the properties of traditional knowledge.
Patent Registration Details
The following steps must be followed while obtaining patent protection:
- Filing: Filing means registering about the invention in specific forms provided in the patent office or through online mode.
- Title: Title must be properly and concisely specified that completely satisfies or indicates the technical details related to the invention.
- Background details: Description of the invention must be stated in clear language with enough details so that a person even with an average understanding of the field could understand and invent something new by the use of that invention.
- Visual materials: Background details must be included with diagrams, such as use case diagrams, flowcharts, graphs to make the study easy to understand.
- Abstract: Brief summary of the invention must be included so that a person could take the idea about the invention without going into further details.
- Field: Type of field must be defined precisely in the “claims” part of the patent application, to give general idea about the subject to which the patent is related to.
To know more about the various forms and fees for different Patent Applications, visit our another service page.
- Supporting documents: While filing various kinds of statements or declarations, supporting documents must be submitted to the patent office so that the invention can be verified and validated on the basis of the resources provided.
- Patent Publication: It takes 18 months (1.5 years) after the priority date to sanction the publication of a patent application. Its publication might also be kept confidential if applicant requested for its secrecy or if it gets withdrawn within the time period of three months before publication date. After published, all the invention details, including drawings and deposits is disclosed publically. The applicant can only get any sort of financial outcome from his/her patent application after it gets granted.
Form 9 is required to be filled if the applicant wants to schedule the publication of his/her application within before 18 months. This allows its publication within a month of filing the request.
- Patent Examination: Applicant has to file request for conducting the examination within 36 months of filing the application. Examiner will then start examining the application, checking all the claims, scope, specifications, language errors, etc., and will submit the report within 1 to 3 month from the filing date. The report will contain all the re-actions that are required to be performed by the applicant.
In case of filing an opposition, both pre- and post-grant oppositions can be filed. Pre-Grant opposition (Section 25(1) and Rule 55 of the Patents Act, 1970) can be filed before the patent got its grant, while Post-Grant opposition (Section 25(2) and Rules 55-62) is required to be filed within 12 months of the patent grant. Oppositions are generally filed when any individual, business, or organization is not satisfied with any aspect of the application. There can be a number of reasons, such as Non-compliance of patentability requirements, Nondisclosure or Wrongful disclosure of genetic resources or traditional knowledge, and Publication, Sale, or Import of the claimed invention before the priority date.
- Patent Duration & Renewal Fees: Every patent in India is valid for 20 years from its filing date, no matter if it is filed with provisional or complete specification. While for applications filed under PCT the term of 20 years begins from International filing date. As per Section 53, Rule 80 of Indian Patents Act, to keep the patent enforceable the renewal fee is to be paid well in advance to the Indian Patent Office. As per Rule 80(2), the patentee is required to correctly quote the date of patent, patent number and the year with respect to which the fees are to be paid.
- Assignment and License: Applications must be filed according to the prescribed format with the Controller for the registration of assignments and license and other related documents, thus creating an interest in a patent in order for the patent to be valid. To make it valid, an assignment or a license must be recorded within six months from the date of the document.
- Infringement: According to Section 48 of the Indian Patents Act, 1970 the patentee is conferred upon with the exclusive right that exclude third parties or entities from making, importing, using, offering for sell or selling the patented invention, product or process without prior approval from the patentee or licensee. Violation of the aforesaid policies or rights constitute of patent infringement.
- Appeal: All appeals are to be made at the High Court within three months from the decision of the Controller.
- Patent attorney: A patent agent or an attorney holds precise knowledge about the timeline, the legal documents, and the legal procedures that must be done while preparing a patent application, and therefore must be consulted.
Patent Registration in India
Get In Touch / Request Free Consultation
Here you can Download our FREE Help Guides:
- Procedure for Patent Registration in India (click here for download access)
- Patent Registration Fees in India (click here for download access)
 Click Here to Get Download Access (All Free Resources)
Click Here to Get Download Access (All Free Resources)